In order to make them more organized and accessible, I’m moving my resources page to a series of blog posts. Here I start with local to Boston food resources, including financially accessible options. High quality, local, wild and accessible food is the foundation of so much, and I want to keep spreading knowledge of resources to folks in my community. Here goes.
This Map of the “urban commons” in Somerville/Cambridge with public food sources. Mulberries and more!
Find a farmer’s market in your neighborhood.
How to use EBT/SNAP at local farmers markets.
The Neighborhood Farm in Needham has been known to have pay-what-you-can boxes available for their fresh produce at farmers markets in JP and Roslindale.
The Daily Table is a not-for-profit grocery store in Dorchester which serves fresh produce and ready-made healthy food. They seem to be opening a new location in Roxbury, as well.
Buckle Farm is where I source most of my and fresh produce year-round. He farms pork, too!
Herbalism and Herbalist Resources
Herbalism and Herbalists
Local gem Bellx of Semilla of Ixchel offers full-spectrum reproductive support, herbal wisdom and customized preparations, and herbalism apprenticeships for People of Color in greater Boston. Offerings include an herbal CSA, placenta medicine, and workshops about holistic healing.
Muddy River Herbals is the project of Jenny Hauf and her husband Matt. They grow and wildcraft local, organic herbs for folks in the Boston area, and can be found at the Roslindale and Melrose Farmers Markets. Much of the calendula in my postpartum sitz baths comes from these guys!
While not local to the northeast, La Loba Loca is an incredible herbalist and friend who offers consultations, workshops, skillshares, knowledge shares, and seedlingships.
Clair Moore is a clinically trained herbalist and professional private chef who provides medicinal food preparation services around Boston, especially allergen-free foods for folks with autoimmune diseases or chronic illnesses. She and Amanda of The Willow Witch have also teamed up to create Willow Provisions, a medicinal herbal food supper club.
Herbstalk is a growing community of herbal classes in the Boston area. Based in Somerville, this yearly conference brings together folks from many herbal traditions every June.
Founded by Katja Swift and Ryn Midura, the CommonWealth Center for Holistic Herbalism in Brookline offers classes, apprenticeships and a clinic for low-income folks who seek herbal care.
Tammi Sweet at the Heartstone Center for Earth Essentials teaches an AMAZING anatomy & physiology class for holistically-minded folks who would otherwise shy away from a science-heavy class. She frequently offers free webinars on a variety of topics from allergies and asthma to the endocannabinoid system.
Clinical Trial on Autoimmune Protocol Diet
When a clinician was inspired by her patient’s very positive reaction to an anti-inflammatory diet, she decided to run a clinical trial of the Autoimmune Protocol Diet with other sufferers of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (or IBD, including both Crohn’s Disease and ulcerative colitis). While the sample size is small, and more research could always be done on the affect of diet on chronic illness, the results from this trial are absolutely incredible. I hope this initial mini-study will inspire folks who suffer from chronic, autoimmune illnesses to take control of their health and seriously consider the importance of food in both the severity and progression of chronic disease.
Fifteen IBD patients completed a trial with the full Autoimmune Protocol Diet (a few dropped out of the study because dietary change is hard). On average, these people were seriously ill with Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis symptoms for almost 20 years. Seven of these participants were already on immunosuppressive medication because of how severe their symptoms were.

As defined by Dr. Sarah Ballantyne of thepaleomom.com, the Autoimmune Protocol Diet focuses on both inclusions of nutrient dense foods, and exclusion of foods that are inflammatory or can harm the gut (and therefore, harm the body’s normal immune function). While the Internet (and real life, if you’re paying attention) contains hundreds and thousands of “anecdotal” stories (mine included) of folks who’ve turned around their chronic illnesses using a similar diet, this is the first-ever “official” clinical trial to be done using this particular approach. I couldn’t be more thrilled.
For the folks in the IBD study, 73% of participants achieved full clinical remission by 6 weeks, and remained in remission through the maintenance period. One participant who did not achieve full remission did note that their joint pain had resolved. For folks who were sick an average of two decades, seeing a nearly 75% remission rate in six weeks is mind blowing. My greatest hope is that this small clinical trial reaches the consciousness of many allopathic practitioners, so that they can truly educate patients about the alternatives and options for managing all kinds of chronic and autoimmune illnesses.
If you’re local to Boston (or want to meet online), and you’re curious about an herbalist’s approach to chronic autoimmune disease, you can reach out anytime for a consultation.
Support Boston Abortion Support Collective this fall!
A Midsummer Cold’s Steam
In an unusual turn of events, I came down with a summer cold in late July. This summer, I had intentionally planned a gap in due dates so I could take some time off, and this well-timed immune dip occurred before I had to attend any labors. Thank goodness.
The cold was tricky for me to kick, however. I rested and drank broth and elderberry tea all day. One of the factors in my slowed ability to fight this cold is my hypothyroid (which approximately ten million Americans also have). Having a slow thyroid makes me run cold, and it’s tricky for my body to build an appropriate fever to kill pathogens. I also tend to be super dry – and this cold definitely exacerbated that for me. When the body produces mucous, it’s actually healing itself. It’s a way your body expels the gunk that’s making you sick. It’s why an herbalist, for a dry cough, may recommend something like mullein (a strong expectorant) rather than cherry bark (a spasmodic cough soother).
I knew what I needed was wet heat. A steam is a way of bringing the medicinal qualities of plants directly to the tissues affected by a cold (mucous membranes in nose, throat, mouth, lungs). After a few days of these steams, I’d kicked the dry cough and was able to move on from my cold.
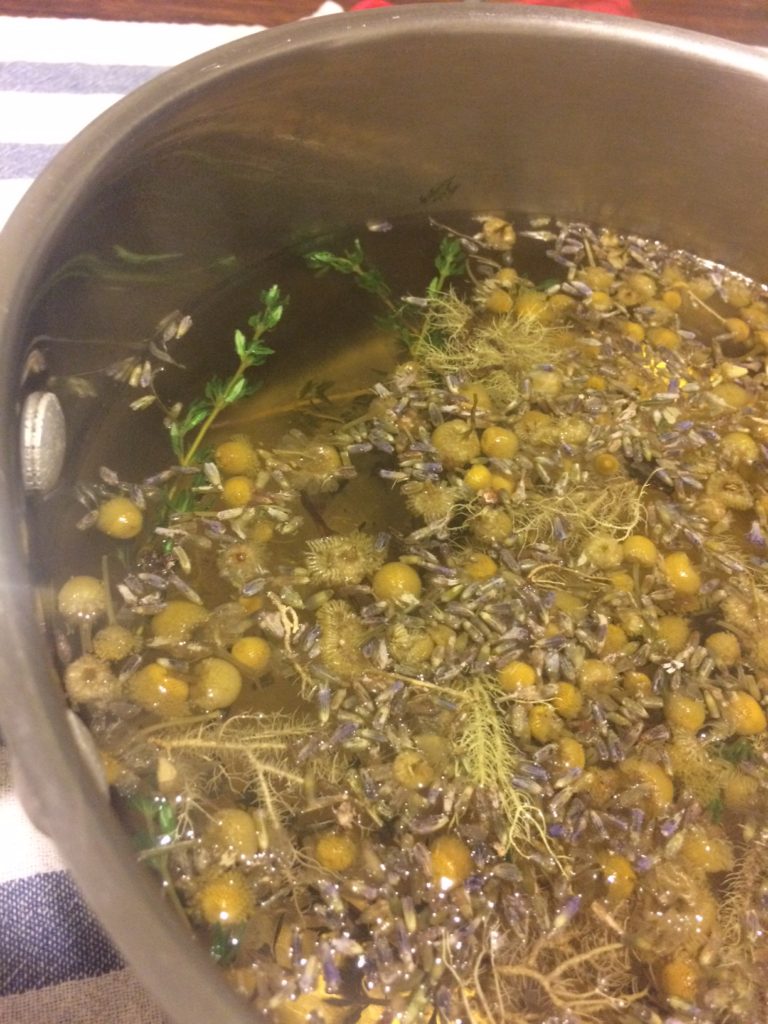 Included in my steam is fresh thyme from the front porch. Aromatic culinary herbs are very effective as antimicrobial and antibacterial agents. The essential oils come out with heat and perfume the air. I also included some usnea, from my friend’s land in Cape Cod. Usnea is a lichen (algae/fungus combo) that grows on trees in woodsy/seaside/oceany places. It’s known to have herbal antibiotic action, and is especially useful for mucous membranes (such as lungs, sinus, or urinary tract). Its constituent, usnic acid, is one of the more studied herbal extracts because it inhibits gram positive bacteria metabolism, making it potentially affective against tuberculosis, staphylococcus, streptococcus, and pneumococcus.
Included in my steam is fresh thyme from the front porch. Aromatic culinary herbs are very effective as antimicrobial and antibacterial agents. The essential oils come out with heat and perfume the air. I also included some usnea, from my friend’s land in Cape Cod. Usnea is a lichen (algae/fungus combo) that grows on trees in woodsy/seaside/oceany places. It’s known to have herbal antibiotic action, and is especially useful for mucous membranes (such as lungs, sinus, or urinary tract). Its constituent, usnic acid, is one of the more studied herbal extracts because it inhibits gram positive bacteria metabolism, making it potentially affective against tuberculosis, staphylococcus, streptococcus, and pneumococcus.
After a few days of thyme and usnea steams, I added in another before bedtime and focused on gently soothing/relaxing herbs. Pictured here – I added chamomile and lavender flowers. Lavender, like thyme, is also very aromatic and its essential oil has antibacterial action. Chamomile, while gently relaxing, also has some antispasmodic action (mostly when drunk as tea). It’s especially nice to add these if a dry cough (or any cold symptom, really) is keeping you awake at night. Quality sleep is important to healing! Remember: some folks are allergic to chamomile, so it’s not for everyone.
To prepare a steam:
- Heat a pot of water to boil and set yourself up a comfortable spot in the meantime. You’ll probably want a hanky or some tissues handy!
- Grab a towel, and place the herbs in a separate bowl. Because essential oils of herbs can dissipate quickly with heat, it is important to add the herbs to the hot water when you’re ready to breathe them in deeply.
- Once the water is boiling, place the pot in your comfy spot, tent a towel over your head with the steaming water underneath, and add your herbs.
- Breathe deeply, using both nose and mouth and focus on the scents of the herbs. Bring them in to your lungs. Come up for cooler breaths if you need to, but you’ll notice the steam making your nose run and your dry cough more productive.
- After about 15 minutes, the scent of the steam may not be as strong. You’ve absorbed the most medicinal parts – yay!
Steams can also be very kid-friendly, and herbs can be customized depending on the particular manifestation of an illness. To make a kid-friendly steam, build a blanket fort and read stories with a flash light in the fort with your steam water nearby, perfuming the area. This way, the direct heat of the steam won’t be too intense, and a kid is more likely to sit in one place for the duration!
My Herbal (and otherwise) UTI Protocol
This post has basically been years in the making. Like many folks, I’m constantly learning what works best for my body, and even that is a moving target over time. Things change, strategies get refined, new products are created, and bacteria get smarter and more resistant to antibiotics as time goes on. Many folks know all about cranberry for its urinary tract supporting affects, but I hope to go in with some more depth today.
As some folks know, I have a chronic kidney condition that informs much of the work I do. Heck – it’s what made me want to become an herbalist in the first place. From my intensive self-care practices between client births, daily herbal tea habit, and still frequent visits to doctors offices for lab works and check-ups, my membranous nephritis is never far from mind. In my experience, having kidney disease does not make me more susceptible to urinary tract infections. However, it does mean that if and when I show UTI symptoms, I may only have a day or two before the bacteria is able to spread to my kidneys. This creates a much more serious problem unless I take All The Precautions.
A word about autoimmunity
There are many people who have other ongoing urinary issues – Interstitial Cystitis, “overactive bladder,” and chronic urinary tract infections are just a few examples. In any of these cases, I highly recommend looking into an individual’s medical history (including family members) and see if there could be a link with autoimmune conditions. While medical science separates autoimmune diseases by many diagnoses, making them seem increasingly “rare”, the mechanism of an overactive immune system that attacks it’s own body’s tissues remains the same. At least 7% of Americans have some form of autoimmune disease, and with high rates of mis-diagnoses, the number is likely even higher. For example, chronic kidney disease is almost nowhere to be found in my family history – but autoimmune diseases (multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus) are increasingly common, and that link is very important.
With an autoimmune connection, I make no recommendation more strongly than researching the so-called Autoimmune Protocol, and identifying individual triggers. Poor digestion and chronic inflammation can lead to “leaky gut” and molecular mimicry. In terms of an overactive immune system, this means that leaked food proteins can potentially be a big factor in the severity of an autoimmune disease. The triggers I avoid include gluten (and all grains except rice), dairy products (casein), canola oil, soy, nightshades, refined sugars, coffee and getting less than 7 hours of sleep in a night. As a birth worker, I never know when I’m going to need to be up all night, so staying on top of everything that is within my control is absolutely necessary!
A little more background
It has been six years since I began to identify and cut out my allergens, developed a daily nettle infusion practice and slowly have seen my kidney inflammation drop to lower and lower levels. While I’m certainly not “cured” of the chronic stuff, I’m getting pretty good at avoiding flare-ups while coping with an unpredictable work schedule. The longer I meander down this path of improvement, the less severe my urinary tract infections are. Instead of needing to go to the emergency room within 24-48 hours, as I did 7-10 years ago, I now have a week or more to really fight off an infection herbally before it gets as deep as my kidneys and necessitates antibiotics.
Movement Matters
Proper alignment is a major factor in repeat UTIs. As Katy Bowman explains in her blog, Nutritious Movement, pelvic alignment is vital for keeping bacteria out of the upper parts of our urinary system. Humans used to walk long distances and have varied movements as we went about our lives. Now, we’re used to tucking our pelvises backwards while sitting in cars in traffic, at office desks, on couches. While this is only one part of the story, chronically mis-placing our urinary tracts can make certain folks more susceptible to urinary tract infections.
Katy also has an excellent post about pregnancy-related balance here.
Dysbiosis
As one of my mentors, Katja Swift, once told us in class (in so many words)- humans have always had urethras near their anuses. We can take all the precautions with wiping in specific directions we want, but that doesn’t change the fact that the problem really comes down to an imbalance of the wrong kinds of bacteria in the wrong kinds of places. It’s becoming more well known that humans are made of 90% bacteria. Yes, urinary tract infections are most often (but not always!) caused by Escherichia coli. Another major consideration is that the average American consumes 130 pounds of sugar per year. This is absolutely unique to this time in human history – we did not evolve to cope with that kind of calorically-dense, nutritiously-devoid stimulant load.
Probiotics are important, but they’re also not the whole story. We need to avoid sugar and empty grain-based carbohydrates, especially when they’re triggers for flare-ups of a chronic condition. Homemade fermented food is a much more diverse source of happy balancing bacteria than any lab-created capsule (that needed to be shipped in a refrigerator truck, by the way). Many simple recipes for ferments are out there.
Another simple way to “diversify” the bacteria in your urinary tract is to actually go out in nature. Katja has brilliantly called this “naked in the dirt,” and says she’s recommended it to many clients. Yes, it’s kind of seasonally-specific, depending on where you live. However – I was once able to fight off a urinary tract infection while swimming in my local turtle pond. I was feeling a urinary tract infection come on, so I went to my doctor to have a urine test. The test came back without a high enough concentration of bacteria to confirm that I needed antibiotics. The count needed is in excess of 100,000, and with my sensitive system I was capable of feeling symptoms with a bacteria count of only 10,000 or so. As the week progressed, I’d guzzled tons of unsweetened cranberry juice and floated my way through the nearby spring-fed pond. I was still feeling symptomatic, and decided to get tested again. The results? “1,000 colony forming units per ml. MIXED FLORA (3 OR MORE COLONY TYPES).” Having multiple mixed colonies of bacteria present gave my body a leg-up when trying to flush out the E. Coli and I ended up not needing those antibiotics, after all.
Your own experience with diet, chronic illness, stress, movement and lifestyle all have a big impact on your body’s own “host defense” in fighting off any infection, including urinary tract infections.
On to the herbs!
Dandelion leaf (Taraxacum off.) is my favorite diuretic herb of all time. It grows abundantly, costs next to nothing, and simply just works. Part of the mechanism of beating a urinary tract infection without antibiotics is physically flushing it out of your system. Staying hydrated is incredibly important, but when your hydration consists of not just water but a dandelion infusion (tea), it also contains vitamins C and B6, thiamin, riboflavin, calcium, iron, potassium and manganese. Other nutrients present in dandelion leaves include folate, magnesium, phosphorus, and copper. The beauty of diuretic herbs is that they support the urinary system, and help the body avoid excess water retention while simultaneously repleting minerals, rather than depleting them (as pharmaceuticals do). Folks who have a sensitivity or allergy to Asteraceae plants, including chamomile, should proceed with caution.
Goldenrod leaf (Solidago canadensis – but your local variety of Goldenrod should do) is also a member of the Aster family. Its yellow flowers bloom in late summer to early fall, causing it to inaccurately be blamed for ragweed allergies. To the contrary, this diuretic plant actually helps relieve seasonal allergies, and can also relieve urinary tract infections. It is a more gentle diuretic than Dandelion, and is known for being a friend of the kidneys. Daily infusions of Goldenrod leaf and flower can be an important part of an anti-UTI herbal plan.
Nettle leaf (Urtica dioica) is my biggest herbal ally for living with chronic kidney disease. It is another nourishing diuretic herb, best served in a long infusion (think an 8 hour overnight tea). Nettle contains high amounts of calcium and iron (the longer you steep your tea, the more of these get extracted into the liquid), as well as magnesium and vitamins A and K. Nettle is great cooked fresh like any leafy green, but daily tea infusions are part of my years-long practice to nourish my body and kidneys in particular.
Marshmallow root (Althaea off.) is best served as a cold infusion. I’ll often add a pinch of Marshmallow root to a long infusion of diuretic herbs. Because I regularly ingest tea like this, the Nettle, Dandelion, Goldenrod would dry me out unless balanced with mucilaginous moisture. Marshmallow root infusion also plays well with unsweetened cranberry juice, which can be intensely astringent to drink in quantity. This soothing, cooling herb can ease the physical discomfort of a urinary tract infection and is great to include in an herbal protocol.
Kava Kava root (Piper methysticum) can be added to a cold infusion with Marshmallow. The famous anti-anxiety herb is also useful for urinary tract infections because it is mildly pain relieving. A little known urinary disinfectant, Kava works well with any of the above herbs as part of a UTI protocol. Generally speaking, I think it’s important to prioritize practicing with herbs that grow locally. However, when weighing the significance of avoiding antibiotics to my longer-term health, I’m willing to find alternatives that grow a bit farther away.
Cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) is a fairly well studied local-to-me berry. Like any dark berry, Cranberry contains the polyphenol proanthocyanidins. These proanthocyanidins have been shown to help flush out E coli specific urinary tract infections. While I’m a big advocate for using plants in their whole (or close to whole) form, an extract of a sugar in the Cranberry, D-mannose has been shown to be very effective when dealing with an E coli UTI. This study shows that for folks who get frequent urinary tract infections, using D-mannose extract before using antibiotics lead to an almost 4 times longer window before getting another UTI (200 days vs. 52.7 days). I have used this type of D-mannose, which is just a dissolvable powder that is fairly tasteless when mixed with water.
A note about preparation
All of the herbal preparations and products I mention here are water-based. Generally speaking, herbs work best when they can come in contact with the tissues being affected. For a urinary tract infection, herbs may be helpful because they’re astringent, analgesic, diuretic, or anti-bacterial, but they should be drunk as tea or used in a bath in order to reach the urinary tract. For deeper infections, or for folks who are prone to kidney problems, internal use of herbs (and D-mannose) will be the most affective. For folks who get UTI symptoms often, consider lifestyle factors (such as diet, bacteria balance, or other chronic conditions that may be inherited), and a topical bath or steam may be affective.
There are so many herbs that can potentially be used to fight a urinary tract infection. This is just an introduction to what works best for me, as someone who has chronic kidney inflammation and desperately wants to avoid antibiotics. If you’re curious to talk more and get an herbalist’s opinion about your specific situation, check out my herbal consultations page.
In Defense of Placenta Encapsulation
Recently, I’ve heard from many clients (and fellow birth workers) about a CDC case of recurrent GBS infection in a newborn whose mother chose to encapsulate and consume her placenta. This rightfully has folks concerned about the process of placenta encapsulation, and curious about the safety of placenta encapsulation in the case of testing positive in pregnancy for Group B Strep.
Here are the highlights of the case, which are important to consider:
- Mom tested negative for GBS at 37 weeks of pregnancy, so was not given the recommended antibiotics in labor for GBS. When given in labor, IV antibiotics quickly cross the placenta. The Evidence Based Birth article states that about 9% of women will test negative but actually be positive during labor (meaning they unknowingly expose their babies to this risk without antibiotics, as the mom in the CDC article did). Also, 16% of women who tested positive will actually be negative during labor, meaning they will receive unnecessary antibiotics.
- Baby was colonized for GBS anyway, needing to spend at least 11 days in the hospital, taking antibiotics. If a baby is born with GBS infection, the hospital should have sent the placenta to pathology to confirm, and then the mother would not have been allowed to release the placenta for encapsulation. This is standard for ANY infection in labor or in the immediate postpartum. I would never process a placenta that was born while an active infection took place in labor, or if a baby had GBS colonization after birth. This is something that all folks who provide placenta encapsulation must check about before moving forward.
- Mom had her placenta encapsulated, method of preparation unknown in this article, and began taking capsules 3 days postpartum
- Baby had recurrent GBS, and was admitted to another hospital 5 days after release from the first
- Mom’s breastmilk tested negative for GBS, but the placenta capsules tested positive
- The CDC case states, “Although transmission from other colonized household members could not be ruled out, the final diagnosis was late-onset GBS disease attributable to high maternal colonization secondary to consumption of GBS-infected placental tissue.”
The doctors came to the conclusion that, because the placenta capsules tested positive for GBS, the mother must have had higher concentrations of the bacteria in her skin or digestive tract, this re-exposing baby to the infection. Group B Strep likes to live in mucous membranes, and there have been a few cases of recurrent GBS that are not-at-all placenta encapsulation related. An adult with an unknown high concentration of GBS could pass it along to a baby with a kiss.
 The company this mother used states they dehydrate the placenta for encapsulation between 115 and 160 degrees. In my practice, I dehydrate a steamed placenta at 145 degrees, and a “raw” placenta at 160 degrees Fahrenheit. The protocol I use is the USDA guidelines for safe meat preservation and dehydration. The article also mentions that a temperature of 130 degrees for 121 minutes is long enough to kill salmonella (implying that other bacteria could be significantly reduced in a similar temperature/amount of time). Whenever I process a placenta, I dehydrate it (keeping it between 145 and 160 degrees) for at least 12 hours. Preliminary research shows that steaming the placenta properly and dehydrating it both have a significant impact on reducing potentially harmful bacteria or pathogens. I always use steamed preparation before dehydrating a placenta if my client tests positive for GBS.
The company this mother used states they dehydrate the placenta for encapsulation between 115 and 160 degrees. In my practice, I dehydrate a steamed placenta at 145 degrees, and a “raw” placenta at 160 degrees Fahrenheit. The protocol I use is the USDA guidelines for safe meat preservation and dehydration. The article also mentions that a temperature of 130 degrees for 121 minutes is long enough to kill salmonella (implying that other bacteria could be significantly reduced in a similar temperature/amount of time). Whenever I process a placenta, I dehydrate it (keeping it between 145 and 160 degrees) for at least 12 hours. Preliminary research shows that steaming the placenta properly and dehydrating it both have a significant impact on reducing potentially harmful bacteria or pathogens. I always use steamed preparation before dehydrating a placenta if my client tests positive for GBS.
This article also says the company in Oregon says storing the placenta capsules at room temperature is ok. I definitely recommend refrigerating the capsules to keep them safe for consumption, because unlike other dehydrated/preserved meat products, the placenta capsules contain no sugar, salt or nitrates to preserve them.
Let’s get one more thing straight: GBS is a common bacteria that humans tend to have in their digestive tracts. About 15-30% of folks will test “positive” for a high concentration in the recto/vaginal area during pregnancy. Human bodies are made up of 90% bacteria – 9 out of 10 of our cells are not actually human DNA but bacteria. Folks are just starting to study how bacteria balance in our guts affects health, and how it varies from culture to culture- especially with our current high usage of antibiotics in the US. In the 1970s and 80s, folks realized a large amount of seemingly healthy babies were getting infections after vaginal births (things like pneumonia and other breathing issues – as this baby in the article did suffer), the CDC realized a high concentration of GBS bacteria in the vaginal canal could “colonize” babies on their way out, thus exposing them to the risk of infection. IV antibiotics in labor became the standard of practice, reducing the likelihood of newborns with GBS infections by 80%.
There are some folks studying probiotics and rates of GBS, either orally or topically: yes, the preliminary studies show we can positively impact healthy bacteria balance with probiotic pantyliners. Early research implies that Group B Strep is kept in check with lactobacillus bacteria, and even garlic. Other studies imply that GBS likes to live in a yeast-friendly environment, so folks who are prone to yeast infections might be more likely to test positive in pregnancy. Either way- GBS does impact a lot of my clients. Folks who hope to avoid an IV in labor often need to accept IV antibiotics to reduce the risk of passing GBS to a newborn.
Krystina Fridlander at Baraka Birth has a lovely thorough blog post outlining a lot of the research available on probiotics and Group B Strep. Read more here.
Herbstalk 2017
Herbstalk 2017 is happening again at the Armory in Somerville on June 3rd and 4th. I’ll be there teaching a class about herbal support for pregnancy loss.
Hospital Choice Matters, A California Infographic
While this infographic is California specific, it goes to show how an individual person, having a low-risk pregnancy with a first baby, is likely to have a very different birthing experience depending on the norms of the hospital/practice they choose. I know people are limited by location, insurance coverage, and other needs, but doing some research into the intervention rates at local hospitals can make a big difference in setting expectations. So can working with a local doula who knows what the norms of various local birth sites are!
I recently finished Jen Kamel’s class The Truth About VBAC and learned, among other things, how hard it can be for an individual provider to calculate their own rates of cesarean section. While an individual may have a low rate of intervention, those rates may double during the weekends when that particular provider is non on-call. Ideally, any consumer of OB/Midwifery care should get to know the rates of intervention between every provider in a practice they choose.
CLPP Conference 2017
The Boston Doula Project will be at CLPP 2017 facilitating two workshops: An Abortion Doula 101, how to support a friend having an abortion, and Boston Doula Project, a Case Study on Reclaiming Space for Black and Indigenous People of Color.




